What is LED?
LED stands for "Light Emitting Diode." It is a semiconductor device that emits light when an electric current passes through it. LEDs are used in a wide range of applications, including lighting, displays, indicators, and more. They are known for their energy efficiency, durability, and long lifespan compared to traditional incandescent or fluorescent bulbs. LEDs come in various colors and can be used in a diverse array of products, from simple indicator lights to sophisticated electronic displays and lighting fixtures.
The Principle of LED lighting
When the electrons and holes in the PN junction of the light-emitting diode recombine, the electrons transition from a high energy level to a low energy level, and the electrons release excess energy in the form of emitted photons (electromagnetic waves), resulting in electroluminescence. The color of the glow is related to the material elements that make up its base. The main constituent elements such as gallium arsenide diode emits red light, gallium phosphide diode emits green light, silicon carbide diode emits yellow light, and gallium nitride diode emits blue light.
Light source comparison
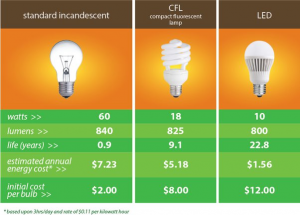
LED: high electro-optical conversion efficiency (nearly 60%), green and environmentally friendly, long life (up to 100,000 hours), low operating voltage (about 3V), no loss of life after repeated switching, small size, low heat generation, high brightness, strong and durable, Easy to dim, various colors, concentrated and stable beam, no delay in startup.
Incandescent lamp: low electro-optical conversion efficiency (about 10%), short life (about 1000 hours), high heating temperature, single color and low color temperature.
Fluorescent lamps: low electro-optical conversion efficiency (about 30%), harmful to the environment (containing harmful elements such as mercury, about 3.5-5mg/unit), non-adjustable brightness (low voltage cannot light up), ultraviolet radiation, flickering phenomenon, slow start-up Slow, the price of rare earth raw materials increases, repeated switching affects the lifespan, and the volume is large.High-pressure gas discharge lamps: consume a lot of power, are unsafe to use, have short lifespan, and have heat dissipation problems. They are mostly used for outdoor lighting.
The advantages of LED
LED is a very small chip encapsulated in epoxy resin, so it is small and lightweight. Generally speaking, the working voltage of LED is 2-3.6V, the working current is 0.02-0.03A, and the power consumption is generally not greater than
0.1W. Under stable and appropriate voltage and current operating conditions, the service life of LEDs can be as long as 100,000 hours.
LED uses cold luminescence technology, which generates much lower heat than ordinary lighting fixtures of the same power. LEDs are made of non-toxic materials, unlike fluorescent lamps that contain mercury, which can cause pollution. At the same time, LEDs can also be recycled and reused.
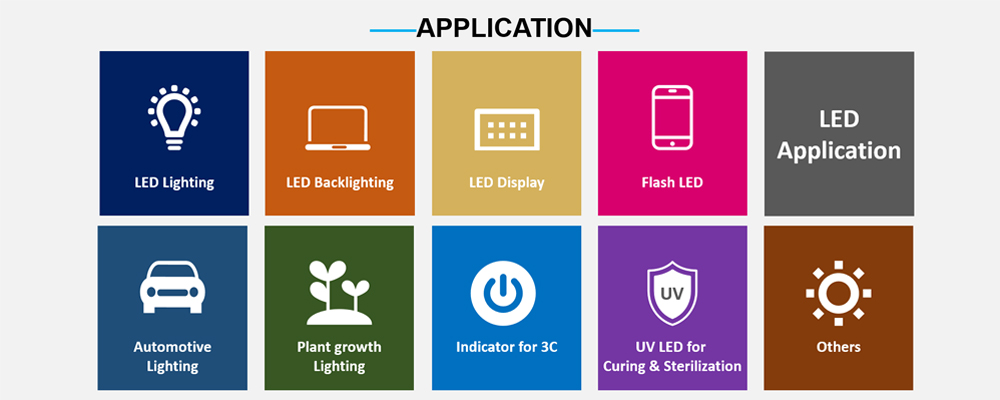
The application of LED
As LED technology continues to mature and develop rapidly, more and more LED applications appear in our daily lives. LEDs are widely used in LED displays, traffic lights, automotive lights, lighting sources, lighting decorations, LCD screen backlights, etc.
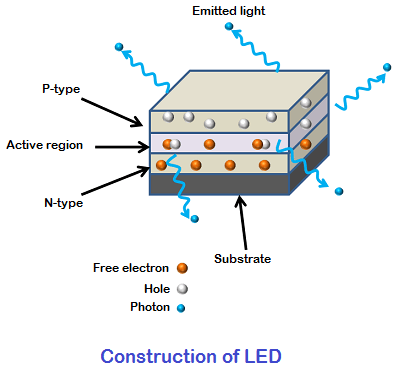
Construction of LED
LED is a light-emitting chip, bracket and wires encapsulated in epoxy resin. It is light, non-toxic and has good shock resistance. LED has a one-way conduction characteristic, and when the reverse voltage is too high, it will cause breakdown of the LED. The main composition structure is shown in the figure:
Post time: Oct-30-2023







