One of the great charms of technology is that it has brought us OLED displays. If you are in the market for a modern display and want it to have the features you expect, then you should definitely explore OLED displays. In this fast-paced era, it is worth knowing the advantages of OLED displays.
What is OLED?
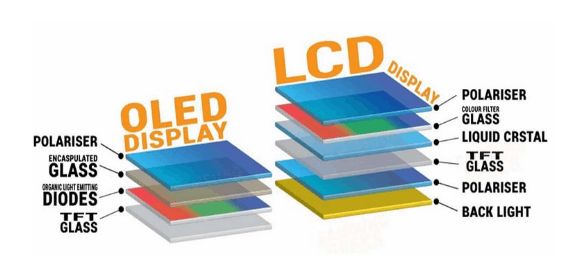
OLED is the abbreviation of "organic light-emitting diode". Another name is "organic electroluminescent diode". It emits light directly through electricity, unlike the traditional way of emitting light by heating the filament with electricity. OLED displays are composed of thin layers of glass, plastic and special organic molecules that react to the electric charge and generate very low heat. Touching the OLED display is almost not warm, which saves a lot of energy, which is a big improvement over the high-energy-consuming CRT displays of the past.
The History of OLED
The discovery of modern OLED technology can be traced back to 1987. At that time, two scientists from Donman Kodak, Steven Van Slyke and Ching Tang, discovered some organic substances that can emit light at low voltage. As early as the 1960s, the discovery of delayed fluorescence paved the way for the birth of OLED. Although early organic materials required high voltage to emit light, Kodak scientists succeeded in achieving fluorescence at low voltage.
These scientists first developed OLEDs with a yellow-green spectrum, then an orange-red spectrum, and finally overcame the energy gap law to successfully achieve red diode emission. Later, as the technology improved, new OLED displays such as AMOLED (active matrix organic light-emitting diode) appeared.
Key Components of an OLED Display
The heart of an OLED display is the OLED emitter. It is an organic component that emits light when electricity is applied. The basic structure includes a layer of material between the anode and cathode. Modern OLED devices have more layers to improve durability and efficiency, but the basic function remains the same. OLED panels are composed of a front panel, a back panel, electrodes, an encapsulation layer, and a substrate. This system is very sensitive to moisture and oxygen, so the encapsulation layer is very complex.
Substrate
The basis of OLED displays is a glass or plastic substrate, a transparent material that provides a stable surface for other components.
Organic Layers
Multiple layers of organic materials are deposited on a substrate, including:
Emitting layer: Contains organic molecules that emit light under electrical stimulation.
Hole transport layer: Transports positive charges (holes) to the emitting layer.
Electron transport layer: Transports negative charges (electrons) to the emitting layer.
Transparent Conductive Layer
This layer is located on both sides of the organic layer and acts as a transparent electrode, allowing current to flow into and out of the organic layer.
Encapsulation Layer
To protect the fragile organic layer from moisture and oxygen, an encapsulation layer is usually applied on top, which consists of a barrier material that prevents environmental factors from affecting the organic layer.
Advantages and Disadvantages of OLED Display
Advantages
- Ultra-thin design: OLED displays are thinner than LCD and LED displays.
- Flexibility: The substrate of OLED can be plastic, making it more flexible.
High brightness: The light-emitting layer is brighter and does not require glass support.
Low energy consumption: No backlight is required, power consumption is lower, and it is suitable for battery-powered devices.
Easy to manufacture: It can be made into large sizes and supports plastic materials, which is easy to expand.
Disadvantages
Color problem: Blue organic materials have a short lifespan.
High manufacturing cost: Moisture may damage the OLED system.
OLED Display Applications
OLED technology has made significant progress in various applications:
Large TVs: OLED TVs are known for their excellent picture quality.
Digital Signage: Used to attract attention in retail stores, restaurants, airports, and more.
Video Wall: A large video wall composed of multiple OLED displays to create an immersive experience.
Heads-up Display: used in motorcycle helmets to provide necessary information without obstructing vision.
Transparent OLED: for automotive displays and augmented reality glasses.
When to Choose an OLED Display for Commercial Applications?
OLED displays offer excellent visual quality for commercial applications where stunning visuals are a priority. Here are some key considerations:
• High-resolution content: OLED displays are an excellent choice when high-resolution images, videos, or graphics need to be displayed.
• Wide viewing angles: OLED displays offer consistent viewing angles, ensuring that content is accurately presented when viewed from different angles.
• Thin and light design: OLED displays are thinner and lighter than traditional LCD displays, making them suitable for applications where space is limited or a sleek design is required.
• Low power consumption: OLED displays are more energy-efficient than LCD displays, reducing operating costs and environmental impact.
If your commercial application requires excellent image quality, wide viewing angles, and sleek design, an OLED display may be the best choice.
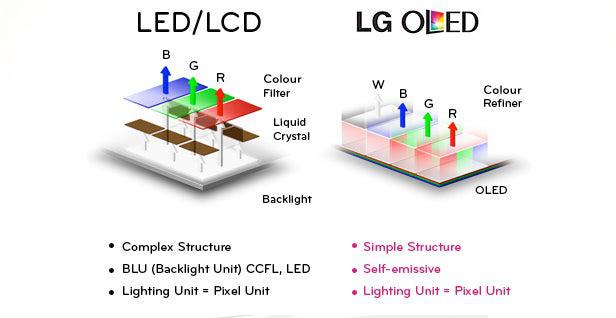
The Difference Between OLED Vs LED/QLED Display
Traditional LED displays are based on LCD technology, a time-tested structure. LCD screens consist of a thin grid of transistors that work using tiny crystal elements. This process involves the regulation of dark and bright pixels, but the actual light emission comes from the storage of LEDs. The best way to test an LCD screen is to use an LED backlight, which allows for higher contrast and better screen dimming, making the display better than previous versions. OLED technology goes a step further, providing eye protection and not causing visual fatigue.
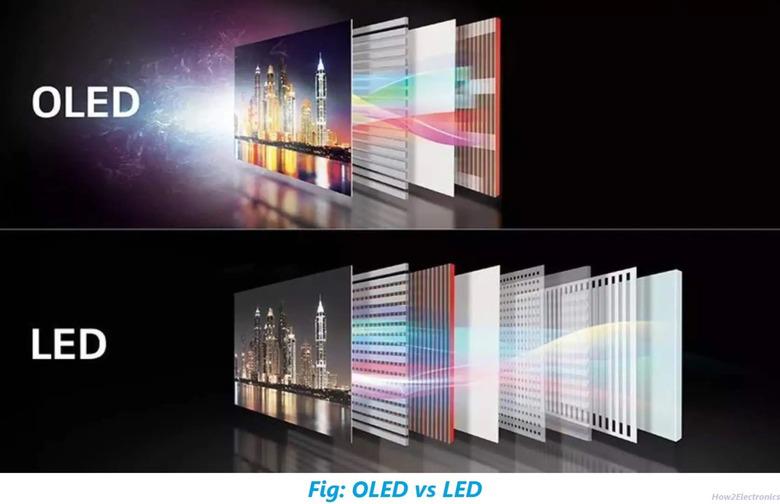

The construction of QLED displays is very different from OLED displays. QLED displays use quantum dots, which produce light when powered, somewhat similar to OLED. But QLED converts the blue light it receives into white light, which is achieved by using red and blue quantum dots. QLED displays are brighter, but also more expensive than OLED and are still in the early stages of development. In contrast, OLED displays are self-luminous, display their own colors, and are less expensive. LED displays, on the other hand, are a panel made of light-emitting diodes, and are commonly used in billboards and signs.
Post time: Oct-21-2024







